Shorenstein Journalism Award Honors Netra News, Spotlights Public Interest Reporting Advancing Democracy and Accountability in Bangladesh
Bangladesh last year staged a rare pivot against a global tide of democratic backsliding. In August 2024, a student-led uprising toppled the country’s long-entrenched authoritarian rule and opened a window for democratic reform. At that turning point, Netra News, Bangladesh's premier independent, investigative journalism platform, rose to the occasion in the role it was built for.
Founded in exile to investigate high-level abuse of power by Bangladesh's regime and press for accountability, Netra News delivered verified, real-time coverage amid internet blackouts and a deadly crackdown by the brutal government of Sheikh Hasina. In the aftermath of Hasina’s ouster, as an interim government has been working to introduce reforms and restore Bangladesh to democratic rule, Netra News’ evidence-driven, nonpartisan reporting helps frame policy debates, establish press freedom, and push for democratic norms.
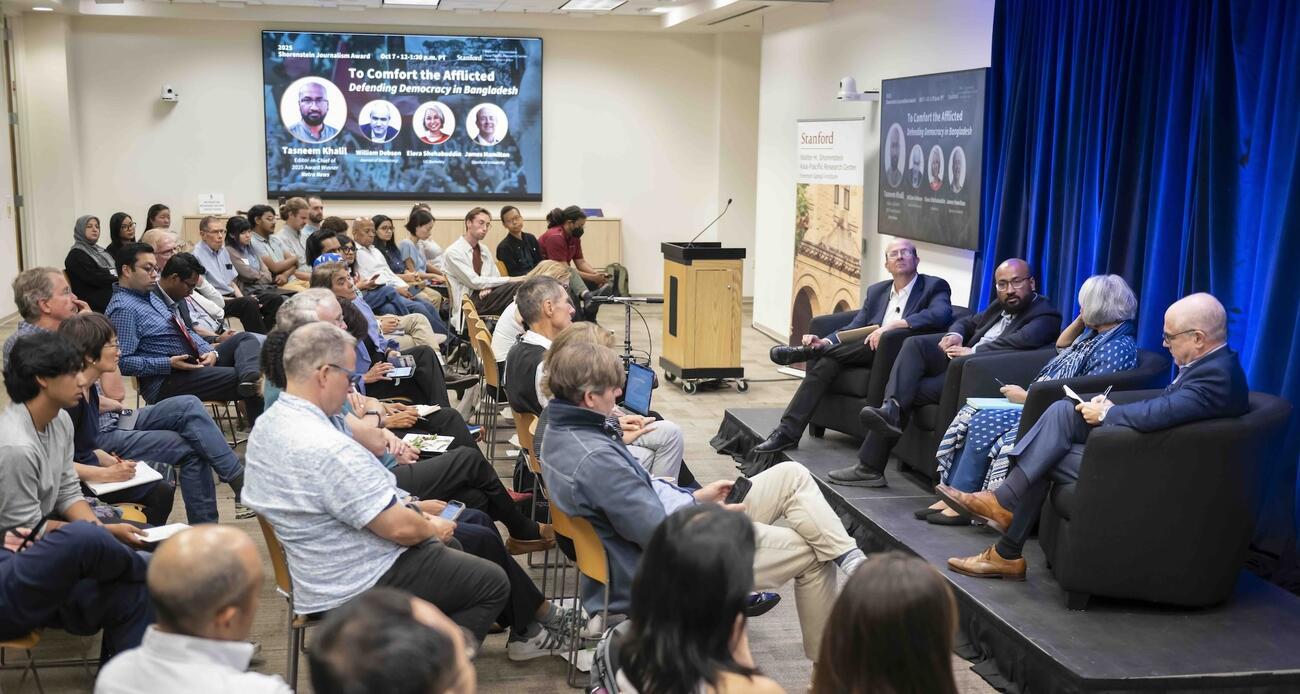
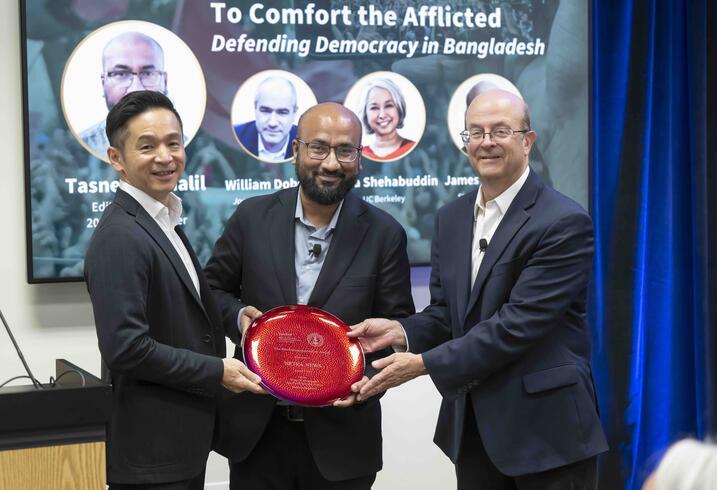
For its courageous reportage and efforts to defend democracy in Bangladesh, Stanford University’s Asia-Pacific Research Center (APARC) honored Netra News with the 2025 Shorenstein Journalism Award, presenting it to Tasneem Khalil, the outlet’s founding editor-in-chief. At the award ceremony, held at Stanford University on October 7, 2025, Khalil delivered a keynote that reflected deeply on the purpose and power of public interest journalism, tracing the philosophy behind Netra News, which he titled “To Comfort the Afflicted and Confront Power.”
To receive insights from our experts and guest speakers, sign up for APARC newsletters >
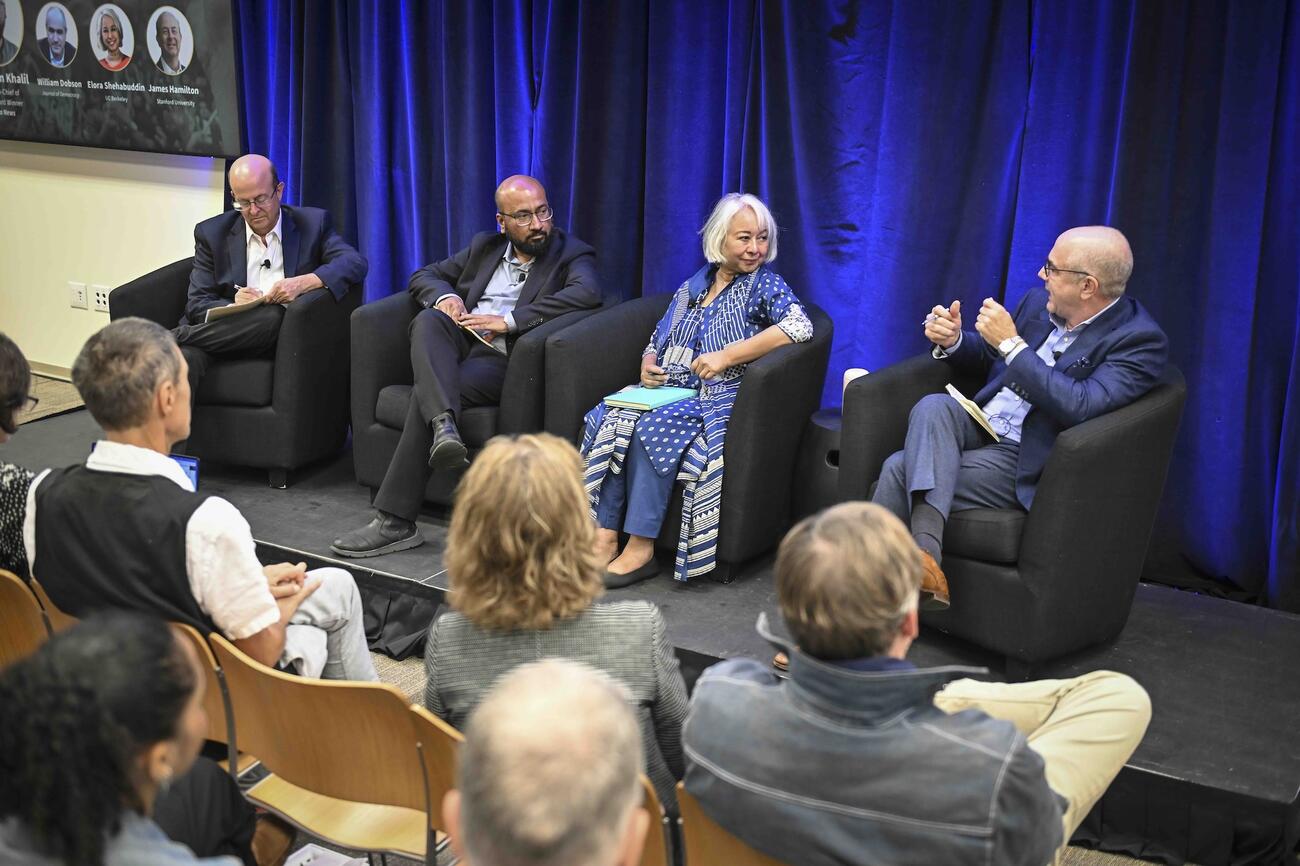
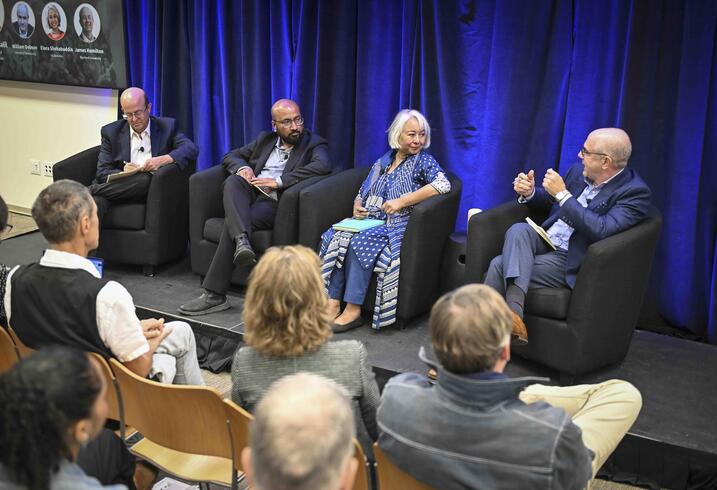
Following his keynote remarks, Khalil joined a panel discussion with William Dobson, the coeditor of the Journal of Democracy and a veteran in international reporting, and Elora Shehabuddin, a professor of gender and women's studies and the director of the Chowdhury Center for Bangladesh Studies at UC Berkeley. James Hamilton, Stanford University’s vice provost for undergraduate education, the Hearst Professor of Communication, and director of the Journalism Program, chaired the discussion. Both Dobson and Hamilton also serve on the judging committee for the Shorenstein Award.
The Shorenstein Award, which carries a cash prize of $10,000, recognizes outstanding journalists and news outlets whose work has deepened the understanding of Asia while advancing the values of a free press.
Bearing Witness
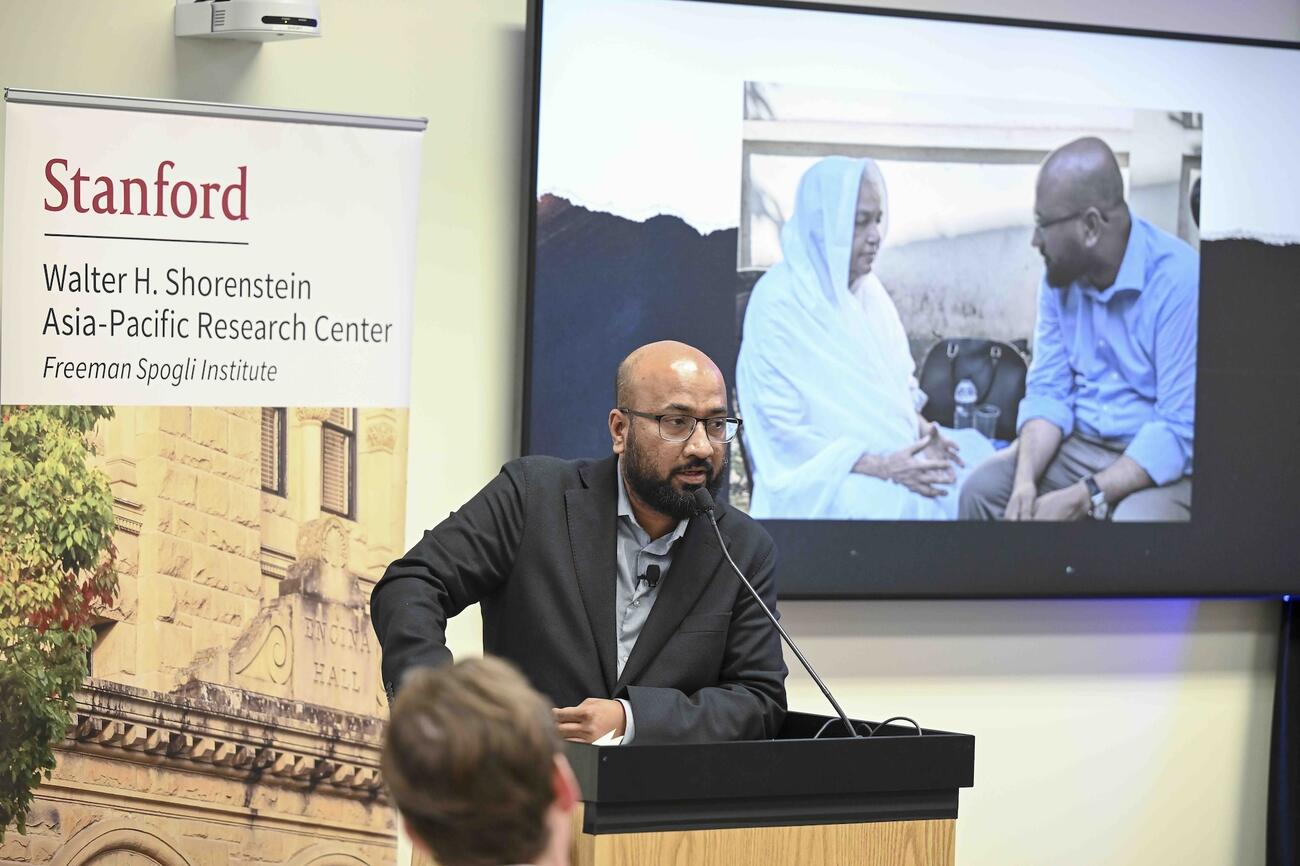
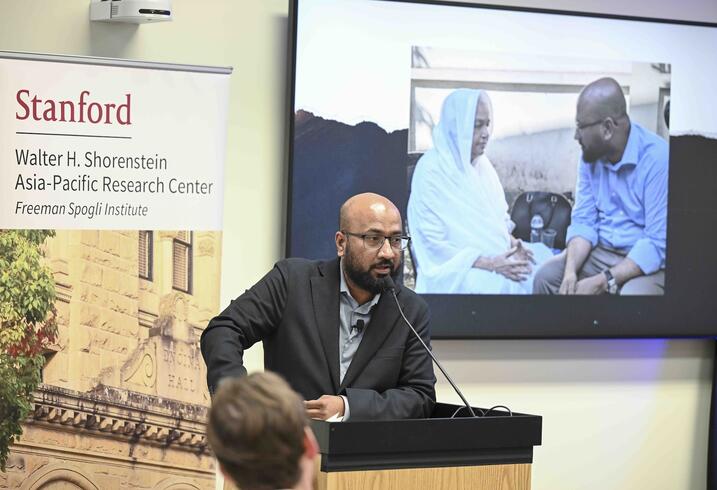
Khalil opened his remarks by sharing a photograph of himself listening to a Bangladeshi woman whose son had been abducted by the Rapid Action Battalion, the country’s elite counterterrorism force that has been accused of serious human rights violations and abuse of power. For Khalil, the image encapsulates the animating question at the heart of Netra News: What does it truly mean to comfort the afflicted?
Investigative journalists, he argued, are first and foremost witnesses. Their work requires listening and documenting, for as long as it takes. He described an investigation that started with a phone call from a day laborer in Malaysia, who recounted his experience being abducted in Dhaka and held in a secret site by a plainclothed squad. Khalil kept calling back with questions, continuing the conversation over months. The source shared precise recollections that helped Netra News map a clandestine detention facility in the heart of the Bangladeshi capital. The investigation, "Secret Prisoners of Dhaka," published in 2023, shed light on hidden abuses and was shortlisted for the Global Shining Light Award for investigative journalism in developing countries.
Khalil described other Netra News investigations that have sought to expose high-level crimes. “Body Count” combined data journalism and fieldwork to analyze more than a decade of alleged extrajudicial killings and acts of torture by Bangladeshi security forces. The patterns revealed which agencies were involved, geographic concentration, and spikes in killings during election cycles, all underscoring a systematic practice. For this work, the newsroom won a 2024 Sigma Award for Data Journalism.
Bearing witness, Khalil noted, means that public interest journalism must listen not only to the afflicted, but also to the perpetrators of horrible crimes. In another project, collaborating with German TV broadcaster Deutsche Welle, Netra News interviewed former Rapid Action Battalion commanders on camera about how extrajudicial killings were carried out. The investigation, "Inside the Death Squad," was the first to provide evidence of targeted killings and torture by the RAB, and was recognized with a 2024 Human Rights Press Award for documentary video.
Another joint investigation with DW exposed a pattern of deploying RAB members implicated in torture and killings to serve as United Nations peacekeepers. The revelations were cited by governments and lawmakers, and intensified scrutiny of peacekeeping vetting practices.
“This is accountability journalism at its purest: reporting that not only informs, but also confronts power and demands justice, said Hamilton in his remarks before the award presentation.
Khalil situated this kind of reportage within a normative framework of journalism that defends democracy and human rights, for which he outlined four roles: monitorial (watching and warning), facilitative (bringing opposing segments of society together), radical (challenging institutions in the name of rights and freedoms), and collaborative (engaging with power when appropriate). First and foremost, this kind of journalism serves the public interest.
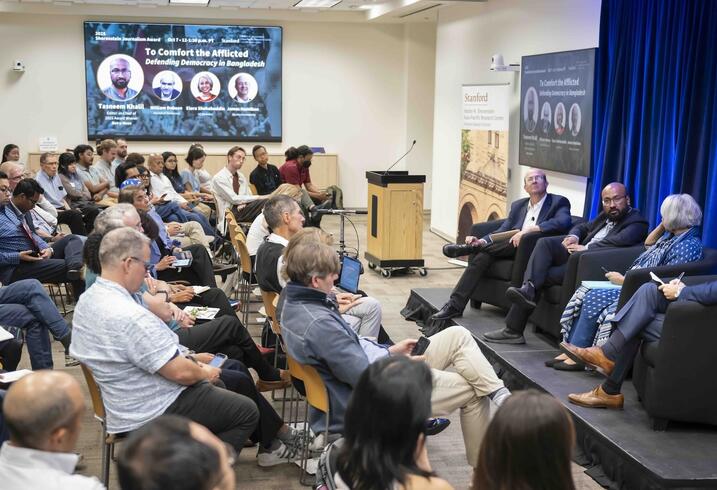





An Experiment in Exile
Those commitments guided Netra News from its inception. Khalii established the outlet in 2019 in Sweden, where he had lived in exile since 2008, seeking refuge following his detention and torture by the Bangladeshi military intelligence agency. As he set up the newsroom in exile with colleagues, he made a deliberate choice: rather than defending democratic norms from afar, they would “cover Bangladesh as if it were a democracy, like Sweden or the United States, and report accordingly.”
That meant reporting with no self-censorship or fear. Due to security risks to staff in-country, Netra News adopted the discipline of an intelligence operation, eschewing daily news coverage and opinions to concentrate instead on meticulously vetted investigations. With its reporters distributed across multiple countries and some working undercover in Bangladesh, the newsroom combined offshore editorial independence with on-the-ground reporting, publishing its investigations in both Bangla and English. This approach uniquely positioned the newsroom to cover the July 2024 uprising in Bangladesh with uncommon access.
Now, a year after mass protests toppled Sheikh Hasina’s authoritarian regime, and 18 years after he fled the country, Khalil has returned to open a Netra News bureau in Dhaka. Receiving the Shorenstein Journalism Award on behalf of the outlet at this moment, he said, is both recognition of its impact since its founding and a signal of support to the next generation of journalists carrying its mission forward.
Youth-Led Uprising in Context
During the discussion that followed Khalil’s keynote, the panelists considered the prospects for democracy in Bangladesh, the economics of investigative reporting, and the dynamics of youth-led protests in Asia.
Asked how the media landscape in Bangladesh had shifted since the 2024 uprising, Khalil said the media’s muscle memory remains one of censorship and fear. The challenge now is to “unlearn stenography,” that is, the practice of reporting only what those in power say, and build habits of dispassionate public interest journalism that scrutinizes both state and non-state power. That includes the interim government, corporate interests, and majoritarian religious forces.
Investigative journalism is a tough business to monetize and sustain. Khalil explained that Netra News is a nonprofit and that grant funding from the National Endowment for Democracy has made it possible. Long-term independence, however, will require earning monetary support from the people it serves. “The ultimate test is asking the public, ‘Will you pay for this?’”
Turning to Gen Z protest movements that have swept across South Asia, Dobson noted a wave of digitally savvy youth mobilizations pressing entrenched elites for substantive change. “People want real change, not shuffling the same roster of political players.” The youth-led uprisings that swept through Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and, more recently, Nepal, explained Dobson, had not originally set out to topple the established regimes, but to fight deepening inequality and economic disparities. The agendas changed, however, due to the lack of responsiveness from political institutions that have been hollowed out by patronage and corruption.
Shehabuddin underscored the central role women activists played in Bangladesh’s 2024 protests, leading from the front to help topple the authoritarian government, only to find themselves largely absent from decision-making led by the interim government.
The event concluded with questions from the audience about journalism in transitional contexts and under strain amid democratic backsliding. Newsrooms should aim to serve the entirety of society, said Khalil, alluding to the fragmented media landscape in the United States. As for standing up to anti-democratic power, he returned to first principles: the media’s charge is to bear witness, especially when those in power disapprove.
Read More
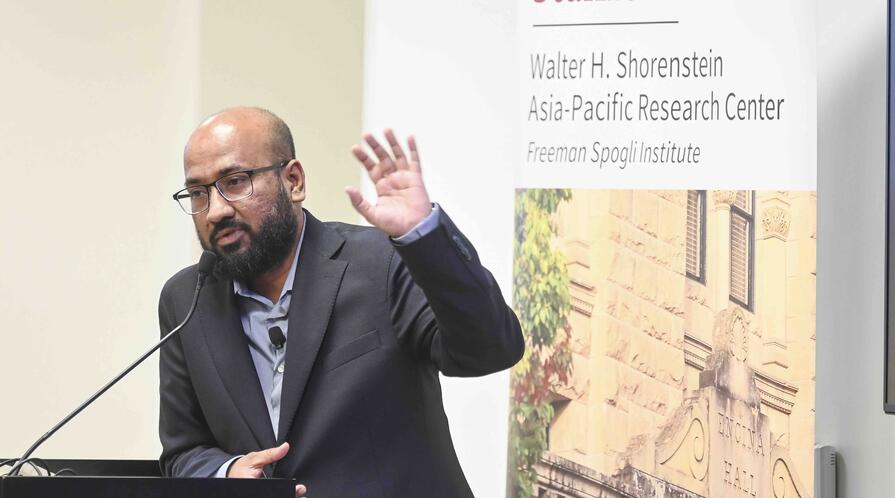

The 2025 Shorenstein Journalism Award recognized Netra News, Bangladesh’s premier independent media outlet, at a celebration featuring Tasneem Khalil, its founding editor-in-chief, who discussed its mission and joined a panel of experts in considering the prospects for democracy in Bangladesh.