Four Insights on How Countries Compete for Talent in a Globalized World
Countries are in a high-stakes competition to develop AI talent and respond to the technology's transformative impact on labor markets and economic growth. As the race intensifies, a critical question looms large: What talent development strategies deliver proven outcomes?
In a recent book published by Stanford University Press, The Four Talent Giants, Stanford sociologist Gi-Wook Shin, a senior fellow at the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies, examines how countries attract, develop, and retain talent in a globalized world. Shin, who is also the William J. Perry Professor of Contemporary Korea and director of the Korea Program at the Shorenstein Asia-Pacific Research Center (APARC), explores how four vastly different Asia-Pacific nations – Japan, Australia, China, and India – rose to economic prominence by pursuing distinct human resource development strategies, encompassing different approaches to education, migration, and transnational talent mobility.
The study provides a framework that extends beyond the four cases, offering policy lessons for other economies, particularly less developed nations. Below are four insights from the book on the evolution of talent strategies and why countries need to construct multiple forms of talent – domestic, foreign, and diasporic – to address new risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities.

1. Look for variation in mobilizing human resources for development
Several Asia-Pacific countries now rank among the world’s largest economies – a marked shift from the 1980s, when Japan was the only regional economy near the top. Shin cautions against interpreting this rise of Asia-Pacific nations as evidence of a single developmental regional “recipe.” Instead, his work shows that similar economic outcomes emerged from different national paths, shaped by distinct histories of colonial rule, nationalism, state-building, and higher education policy.
Rather than isolating one driver of growth, the analysis highlights how states structured education systems, migration pathways, and global connections to talent in ways that reflected domestic priorities and constraints.
2. Talent includes social capital, not just skills or credentials
Shin defines talent broadly as both human capital and social capital. In a transnational era, the value of talent lies not only in technical expertise but also in the networks, relationships, and institutional ties that connect individuals across borders.
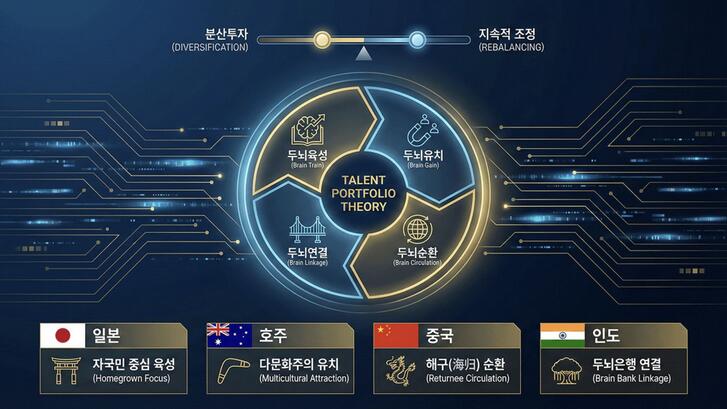
This insight underpins a four-part framework for national talent strategies: brain train (developing domestic talent), brain gain (attracting foreign talent), brain linkage (maintaining ties with citizens and students abroad), and brain circulation (sending talent out and facilitating return). Successful countries rarely rely on a single approach; instead, they combine these strategies in different proportions over time.
Related Story | How Strategic Human Resource Development Helped Build Asia-Pacific Economic Giants.
3. Talent strategies must be diversified and rebalanced over time
A central contribution of Shin’s book is a framework he calls Talent Portfolio Theory, which likens national talent strategies to investment portfolios. Just as investors diversify assets and rebalance them as conditions change, states must continually adjust how they train, attract, and retain talent in response to economic shifts.
Japan’s experience illustrates both the strengths and limits of a concentrated strategy. Its post-WWII success rested on a robust domestic training system spanning universities, vocational schools, and workplace education. Nevertheless, as the global knowledge economy evolved in the 1990s, Japan struggled to adapt, facing demographic decline and hampered by institutional introspection. Only in the 2010s did Japanese policymakers begin to diversify talent development through study-abroad programs, attracting international students, and implementing limited immigration reforms.
Australia followed a contrasting path, relying heavily on foreign talent through skilled migration and international education. Its system emphasized work-migration pathways and relatively easy naturalization for international students, while more recent policies have focused on sustaining global alumni and diaspora networks. Each model carries risks, but together they demonstrate why diversification and timely rebalancing matter.
4. Political leadership and state policy shape talent outcomes
Across cases, Shin argues that talent strategies are not purely organic market outcomes. Political leadership and state capacity play decisive roles in shaping higher education systems and migration policy. China’s post-reform experience demonstrates how state-led overseas training and return programs helped address the loss of scientific expertise after the Cultural Revolution. Over time, China shifted from emphasizing the return of Chinese nationals to the country toward building broader transnational linkage and circulation mechanisms.
India offers a different model, where long-standing patterns of outward migration produced a global diaspora that functions as a form of “brain deposit.” Alumni of Indian Institutes of Technology and other elite institutions now serve as transnational bridges connecting India to Silicon Valley and other innovation hubs.
For developing countries, Shin offers a counterintuitive lesson: initial brain drain is often unavoidable and can be productive if governments invest in long-term linkage and circulation rather than restricting mobility. To the United States and other nations grappling with anti-immigration politics, Shin’s message is that erecting barriers to attracting and retaining global talent could undermine their long-term economic competitiveness.
Read More

From the practices of higher education institutions to diaspora networks, talent return programs, and immigration policies of central governments, a comparative analysis by Stanford sociologist Gi-Wook Shin shows how different national human resource strategies shape economic success.

 FSI researchers consider international development from a variety of angles. They analyze ideas such as how public action and good governance are cornerstones of economic prosperity in Mexico and how investments in high school education will improve China’s economy.
FSI researchers consider international development from a variety of angles. They analyze ideas such as how public action and good governance are cornerstones of economic prosperity in Mexico and how investments in high school education will improve China’s economy.